Conventional NDT
Conventional NDT methods are procedures that have become well-documented in codes, standards, and best practices due to years of use in the field. Compared to newer NDT methods, the process and techniques of a conventional approach are usually more straightforward.
Prime Inspections offers a wide range of conventional NDT methods to target underlying problems that can lead to productivity loss, failures, and catastrophic events.
Target Underlying Problems
Detection of Surface and Subsurface Defects
Internal Defect Detection
Weld Inspection
Corrosion Detection
Structural Integrity Assessment
Thickness Measurement
The Benefits of Conventional NDT
Conventional nondestructive testing (NDT) methods offer numerous benefits, making them indispensable for the oil and gas industry. A few benefits include:
Proven Track Record
These methods, including radiographic testing, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant testing, have a proven track record of reliability and are widely accepted due to their established industry standards.
Cost Effective
Often, it requires lower initial investments and the utilization of existing infrastructure and trained personnel.
Accessibility
It offers a wide variety of equipment and a large pool of skilled technicians. These methods are familiar to many technicians, simplifying the learning curve and ensuring ease of use and interpretation.
Versatility
Enabling applications across a wide range of materials and structures, while their most robust and durable equipment can withstand harsh industrial environments.
Overall, these benefits underscore the importance and effectiveness of conventional NDT methods in ensuring the safety and integrity of critical infrastructure.
Conventional NDT Methods
-

Radiographic Testing (RT)
Radiographic Testing (RT) involves using either X-rays or gamma rays to view a component's internal structure. It is highly reproducible, can be used on a variety of materials, and can store the data gathered for later analysis. Radiography is an effective tool that requires very little surface preparation. Moreover, many radiographic systems are portable, which allows for use in the field and at elevated positions.
-

Manual Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Manual Ultrasonic Testing (MUT) is a form of nondestructive testing typically used to detect volumetric flaws, material integrity, and component thickness. This common form of ultrasonic testing is used to inspect castings, forgings, welded components, and composite structures in all industry sectors.
-

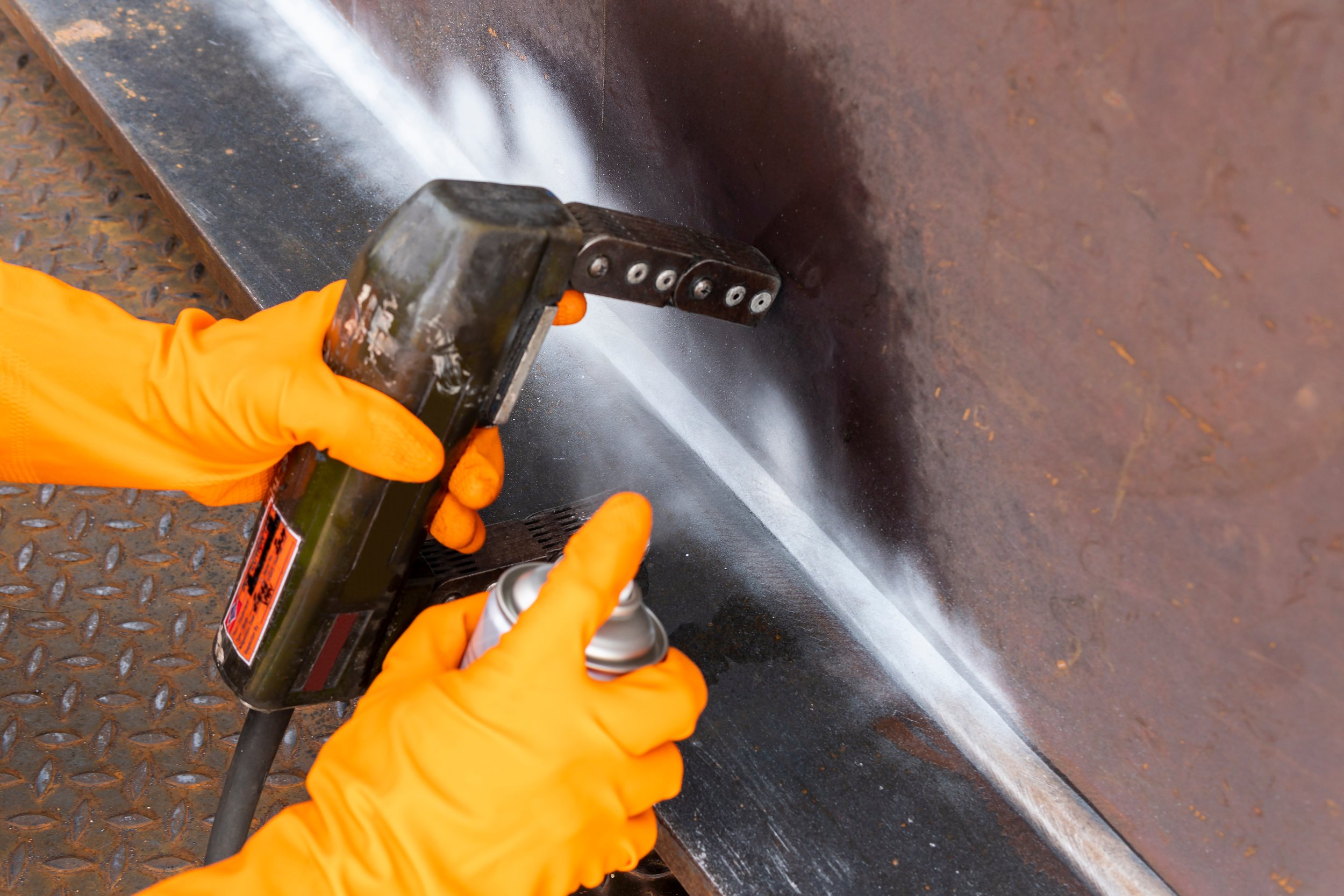
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) is used to detect surface and subsurface flaws in most ferromagnetic materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, and some of their alloys. With little surface preparation required, conducting MT is fast and easy. By applying a magnetic field to the material, any present defects distort the field, causing magnetic particles applied to the surface to accumulate at these locations. The resulting visible indications allow for identifying flaws such as cracks, seams, and other discontinuities. MT is widely used for its quick results and effectiveness in inspecting various ferromagnetic components and structures.
-

Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
Liquid penetrant testing (PT) is a non-destructive testing (NDT) method used to detect surface defects in non-porous materials. In PT, a visible or fluorescent liquid is applied to the surface, penetrating any defects. After a specific soaking time, the excess liquid is removed, and a developer is applied, drawing the penetrant out of the defects to create a visible indication. This method effectively identifies cracks, porosity, and other surface discontinuities in materials like metals, plastics, and ceramics.
-

Hardness Testing
Hardness Testing determines material characteristics such as strength, ductility, and wear resistance. It might be conducted to determine a material's suitability for a given application or conformance to a specification, standard, or particular treatment (heat treatment, thermal process).
-

Visual Inspection
Visual Inspection is an effective NDT testing technique for detecting surface defects to inspect castings, forgings, machined components, and welds. This method involves the visual observation of the surface of a test object to evaluate the presence of surface discontinuities such as corrosion, misalignment of parts, physical damage, and cracks. Visual inspection is conducted by observing the test piece directly or by using optical tools such as magnifying glasses, mirrors, borescopes, and computer-assisted viewing systems.

Complete Inspection Reports
The most important aspect of any inspection service is the final report provided to the customer.
In general, at the completion of an inspection job, we will supply the customer with a final report that includes the following:
It meets the documentation requirements
All important codes and standards included
Quality and acceptance levels for various NDT findings
Drawings, scans, photos, and other visualized data
Inspection summaries and recommendations
Our Conventional NDT Equipment
Sentinel 880 Delta Camera - Iridium 192
Spec 150 Camera - Iridium 192
Dakota NDT - Flaw Detector Series
Olympus 38DL Plus
AGFA Chemicals - Structurix X-Ray Film
AGFA Film Class I & II
70 mm, 90 mm in 4x10 / 4x17 cut film